파일 전송
THIS PAGE IS DEPRECATED: READ File transfer
어떻게 사용해야 할까요?
안드로이드
안드로이드에서 누군가와 대화할 때, 당신은 장치에 사진을 보내거나 이 버튼으로 사진을 찍을 수 있습니다.

참고
When you send a file, the other has to accept it. At this moment you will see ‘awaiting peer’:
[Android_waiting_peer] (https://git.jami.net/savoirfairelinux/jami-project/uploads/56f0316c945ca243448668ae9091b1de/Android_waiting_peer.png)
어떻게 작동하는 거죠?
어떻게 작동하는지
소개
자미는 유통된 응용 프로그램이며 인터넷 연결 없이 작동해야 합니다. 그래서 파일 전송도 마찬가지입니다. 기본적으로 우리는 파일 전송과 전화를 수행하는 것과 같은 방법을 사용합니다. 그러나 TCP에서. 어떻게 작동하는지 요약하기 위해, 우리는 앨리스 (A) 가 보브 (B) 에게 파일을 전송하려는 상황을 상상할 수 있습니다.
First, Alice will request a connection to Bob. To do that, Jami is using ICE (RFC 6544), a protocol used to negotiate links between peers. Alice will send, into an encrypted packet via the DHT the IP address of its device. So, when Bob receives the IP addresses of Alice, they will be able to negotiate a transport where Bob will be able to send packets to Alice. The negotiation can be successful, but if it fails, a TURN server will be used (the one configured into the settings) to perform the transfer. If the negotiation succeeds, Bob will send its IP addresses to Alice to perform the negotiation in the other direction. Note that the link is still not secure, so Bob will send the IP addresses through the DHT network in an encrypted message. If the second negotiation fails, the TURN will be used as a fallback.
이제 이방향 TCP 링크가 여기에 있기 때문에 다음 단계는 A.L.S. 1.3 (일반적으로 TLS 1.3 (TLS1.3) - DHE-FFDHE8192) - RSA-PSS-RSAE-SHA384) - A.S.-256-GCM를 A.L.S.와 B.B. 사이에 협상하는 것입니다.
첫 번째 부분은 파일의 내용을 설명하는 작은 헤더가 될 것입니다. 그리고 밥이 이적을 승인하면 전체 파일이 전송됩니다.
프로세스
파일 전송
다음 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
A client will call
DataTransferFacade::sendFile().DataTransferFacadeis the class corresponding to the API exposed for the clients. It is used to manage a view of the file transfers (the corresponding classes areDataTransfer,IncomingFileTransfer,OutgoingFileTransferandSubOutgoingFileTransfer). This method will ask the linkedJamiAccountto request a connection.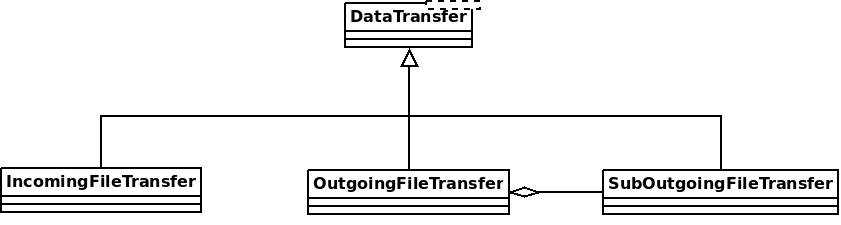
The method
DhtPeerConnector: requestConnection()is triggered and creates a connection between all connected devices of the peer (found on the DHT).DhtPeerConnectoris used to manage the main event loop which manage connections. When a device is found, the event loop will create aClientConnector(which manage the connection for one device) and launch theprocess()method.This method is used to initialize the ICE transport and put a PeerConnectionMsg (which contains the SDP message, see below) on the DHT and waits for a response (
DhtPeerConnector::Impl::onResponseMsg).Then a response is received from the DHT, which contains public addresses of the peer device. We can now negotiate a TLS link (directly via ICE, or via TURN as a fallback). This
TlsSocketEndpointis given to thePeerConnectionobject as an output and the transfer can start.When the TLS socket is ready, the callback
DataTransferFacade::Impl::onConnectionRequestReplyis called, and aOutgoingFileTransferis linked to thePeerConnectionas an input. ThisOutgoingFileTransfercontains a list ofSubOutgoingFileTransfer(one per device) where each sub transfer is a transfer to one device. We do that to be able to furnish the most optimistic view of the transfer (if a contact as 3 devices, where the contact cancel the transfer on one device, but accepted the transfer on the two others, the most advanced transfer will be shown).The
SubOutgoingFileTransferwill first transfer the header of the file, wait the peer acceptance (A “GO\n” message on the socket) and then will send the file.If a cancel is received from the peer or the client or if the file transfer finish, the connection will be closed via a
CANCELmessage on theDhtPeerConnector::eventLoop()and the resources will be released.
[TLSsocketEndpoint](이미즈/파일 전송-tlssocketendpoint-diagram.png)
파일 수신
파일 수신에는 동일한 구조가 사용되지만 방법은 약간 변경됩니다.
JamiAccount클래스는 DHT로부터 메시지를 수신하는데 사용되며, 첫 번째 수신은 DHT 요청이 될 것이기 때문이다.그 다음, 이 메시지는 이벤트 로프를 통해
DhtPeerConnector: onRequestMessage()에게 전달된다.DhtPeerConnector::Impl::answerToRequest는 TURN 서버에 연결하여 ICE 운송을 초기화하려고 노력합니다. 이 방법은 TURN 서버에 2 개의 제어 연결을 열 (IPv4 피어 권한을 부여하기 위해 하나, IPv6 피어에 대한 다른 하나는 RFC 6156로 인해) 이미 열리지 않으면 연결을 허용하고 피어 공개 주소 연결을 허용합니다. 그러면 수신된 SDP는 ICE 후보자를 포함하지 않으면 TURN을 사용하여 피어를 기다리는 SDP 답변을 작성합니다. SDP는 ICE 후보자를 포함하면, 방법은 링크를 협상하려고 노력합니다 (또는 TURN에 대한 후퇴) 그리고 SDP에 응답합니다 (ICE 후보와 함께 또는 그렇지 않습니다).링크가 준비되면, 송신자와 마찬가지로 TLS 링크가 협상되고
PeerConnection에 주어집니다.IncomingFileTransfer에 입력됩니다. 파일의 헤더가 도착하고 클라이언트는 이제 전송을 받아들이거나 취소 할 수 있습니다.
이전 파일 전송을 다시 요청
As specified in Other mime types, the data-transfer interactions are now synced and stored into conversations. So, a device can easily detects if a file was downloaded or not. If not, it can asks all members in the conversation to transmits the file again.
이를 위해, 장치가 mime 타입의 json를 보내게 됩니다: 애플리케이션/데이터 전송 요청+json, 대화의 아이디 ('), 상호 작용 ( (관련 상호 작용), 장치Id, 파일을 수신하는 장치.
송신자는 이제 기기가 발표된 동료의 장치인지 기기가 대화의 구성원인지 확인하고 고전적인 파일 전송을 통해 파일을 전송할 수 있습니다.
수신자는 이제 첫 번째 수신 전송을 받아서 파일을 다운로드하고 sha3sum가 올바른지 확인할 수 있습니다.
계획
[사진: 주요 스케마 다이어그램]
DHT를 통해 SDP가 전송
0d04b932
7c33834e7cf944bf0e367b47
H6e6ca682 1 TCP 2130706431 2607:fad8:4:6:9eb6:d0ff:dead:c0de 50693 typ host tcptype passive
H6e6ca682 1 TCP 2130706431 2607:fad8:4:6:9eb6:d0ff:dead:c0de 9 typ host tcptype active
H42c1b577 1 TCP 2130706431 fe80::9eb6:d0ff:fee7:1412 50693 typ host tcptype passive
H42c1b577 1 TCP 2130706431 fe80::9eb6:d0ff:fee7:1412 9 typ host tcptype active
Hc0a8007e 1 TCP 2130706431 192.168.0.123 42751 typ host tcptype passive
Hc0a8007e 1 TCP 2130706431 192.168.0.123 9 typ host tcptype active
Sc0a8007e 1 TCP 1694498815 X.X.X.X 42751 typ srflx tcptype passive
Z.Z.Z.Z:YYYY
A.A.A.A:YYYY
Where 0d04b932 is the ufrag and 7c33834e7cf944bf0e367b47 the password of the ICE session.
2130706431 and 1694498815 are the priority of the candidates.
192.168.0.126 42751 typ host tcptype passive is a passive host candidate and 1694498815 X.X.X.X 42751 typ srflx tcptype passive a passive host reflecting the public IP address (mapped via UPnP for example).
다중 장치
A user can link its account to several devices. So, we need to implement the transfer when a user send a file to a contact who have multiple devices linked to this account.
첫 번째 접근법
첫 번째 접근 방법은 DHT를 통해 모든 장치에 요청을 보내고 응답하는 첫 번째 장치가 파일을 전송하도록 하는 것입니다. 이것은 연락처에게 좋지 않습니다. 왜냐하면 어떤 장치가 전송을 받을지 알지 못하기 때문입니다.
현재 접근 방식
이제 우리는 여전히 모든 장치에 요청을 보내는데 차이점은 모든 장치가 파일을 수신하는 통지와 전송을 받아들일/ 거부할 수 있다는 것입니다. 그 코드의 주요 부분은 data_transfer.cpp에서 있습니다.
Now (since https://review.jami.net/c/jami-daemon/+/9327), when a user send a file, it will request a PeerConnection with all peer devices. And for all connections, we attach a new input stream to have the ability to accept/refuse/cancel each transfer separately.
data_transfer.cpp에서는 클라이언트에 표시하는 낙관적인 시각을 나타내는 OptimisticMetaOutgoingInfo 클래스를 정의합니다. 그것은 낙관적입니다. 왜냐하면 연락처가 한 장치에서 전송을 받아들이고 다른 장치에서 거부하면 이 클래스는 계속되는 파일 전송을 표시합니다. 모든 장치가 전송을 거부하면만 오류를 표시합니다.
이 클래스는 SubOutgoingFileTransfer와 연결되어 있으며, 이는 하나의 장치로 전송의 상태를 나타냅니다. 클라이언트는 나중에 낙관적인 대신 하위 전송을 보여줄 수 있습니다 (TODO 목록을 참조).
다른 TURN 서버를 사용
Actually the default TURN server is turn.jami.net. But you can host your own TURN server. For example by running a coTURN server.
`sudo ターンサーバー -a -v -n -u 사용자: 비밀번호 -r “현”
Then, you can configure the TURN server in the advanced settings of the app.
참고
This needs some technical knowledge. Moreover, the TURN server should see the same IP address of your node as the destination node, or the peer connection will fail (because the authorization will be incorrect).
전체 목록
Use libtorrent?
출력 파일의 하위 전송 상태를 표시